If you have been watching Power BI news recently, you know that Power BI fields now support custom formatting. In this short blog article, I am going to explain how to use this feature to achieve your custom formatting. You can do things like showing () for negative values, showing custom date/time formats, and etc. Let’s see how this works. If you like to learn more about Power BI, read Power BI book from Rookie to Rock Star.
How to Set Format for a Field or Measure
By default the format of fields/measure is general. That means, a field like OrderQuantity, might look like below in a Power BI visual: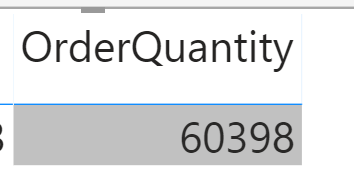
If you want to set the formatting for a field, or measure, you can do it in two different places:
Setting the Format in the Modeling tab
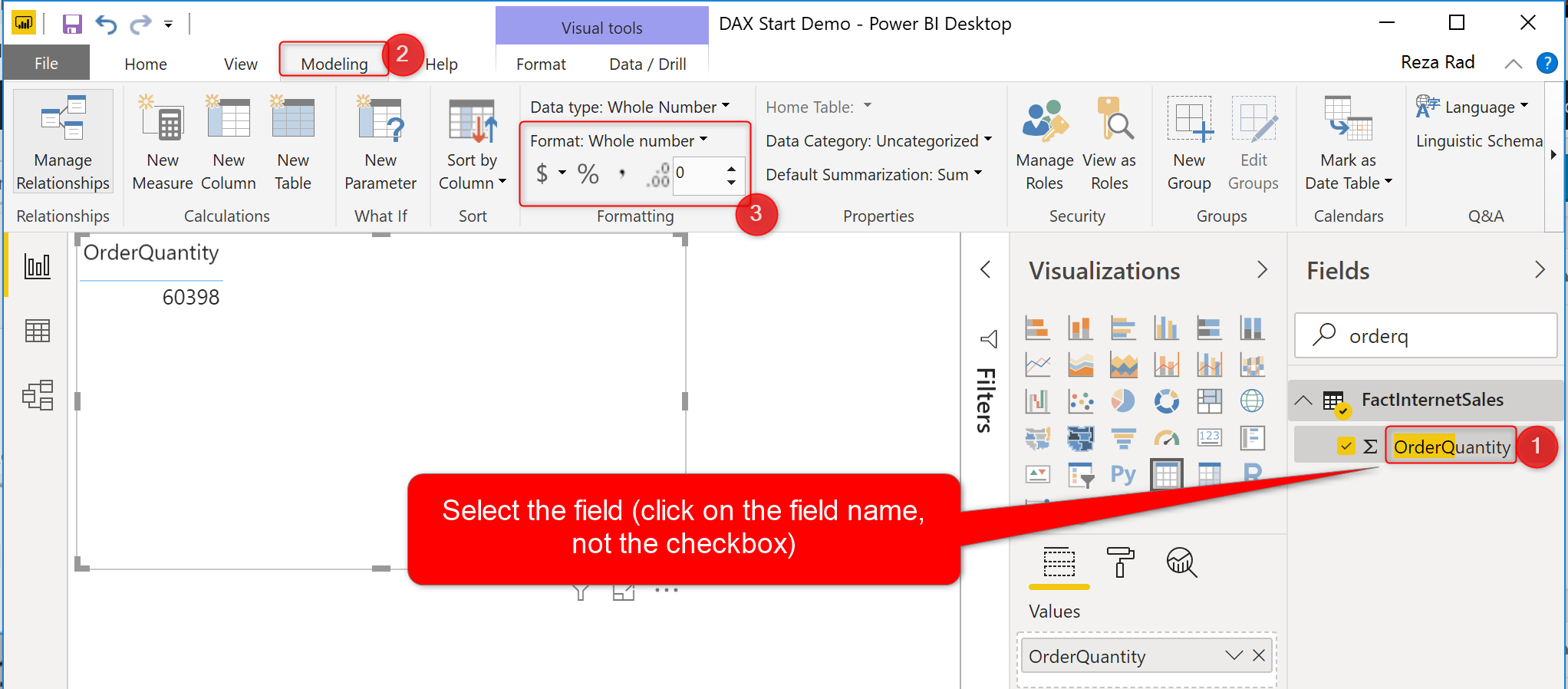
If you are in the Report tab or Data tab in Power BI Desktop, you can select the field (note that selecting the field, doesn’t mean the checkbox, it means click on the text name of the field or measure), and then go to the Modeling tab, and you will see the formatting options there.
Setting the Format in the Model tab
The better place to set the formatting for a field or measure is the format tab. Here you can select a field or measure, then under the Formatting, you’ll see all the options.
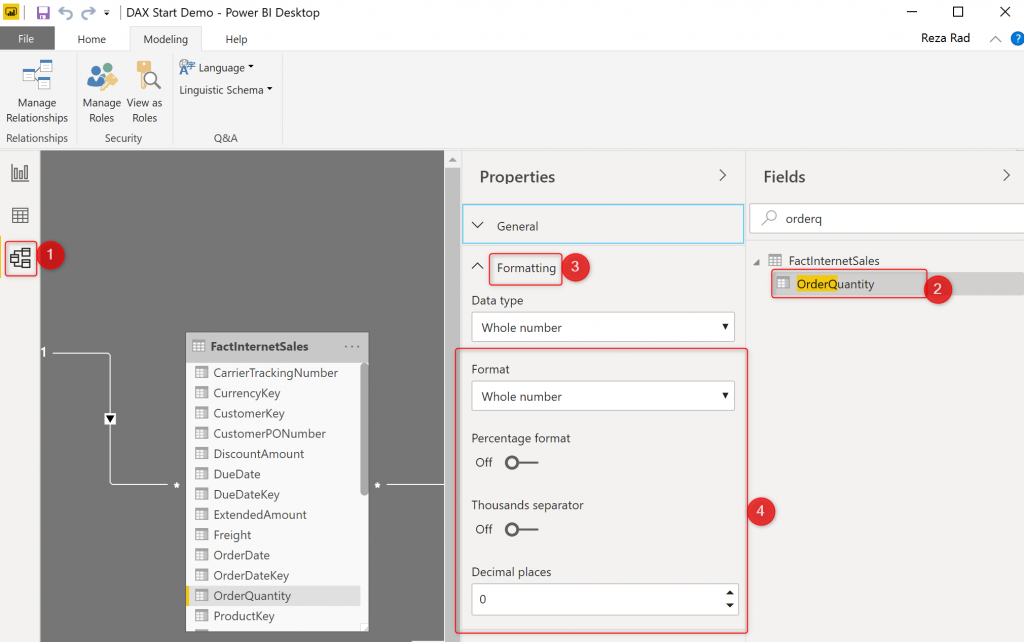
You can set the formatting on whatever you want with Thousands separator, or decimal places (for date and time fields you will have other options too);
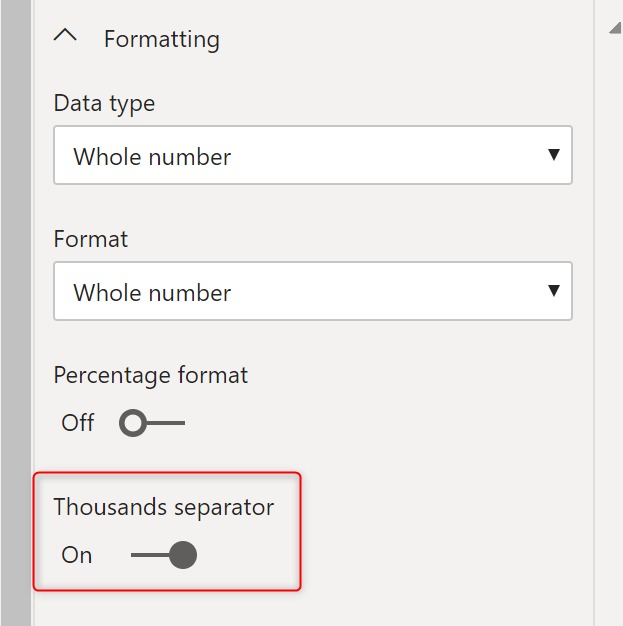
This would make your visualization better based on that selected format
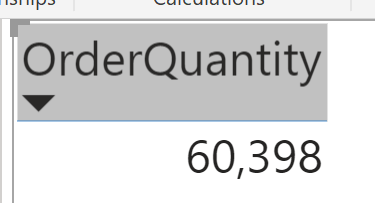
Default Format options
There are some default formatting options for each data type. For Numeric Fields, you have seen the options above. For date and time fields, there are other options:
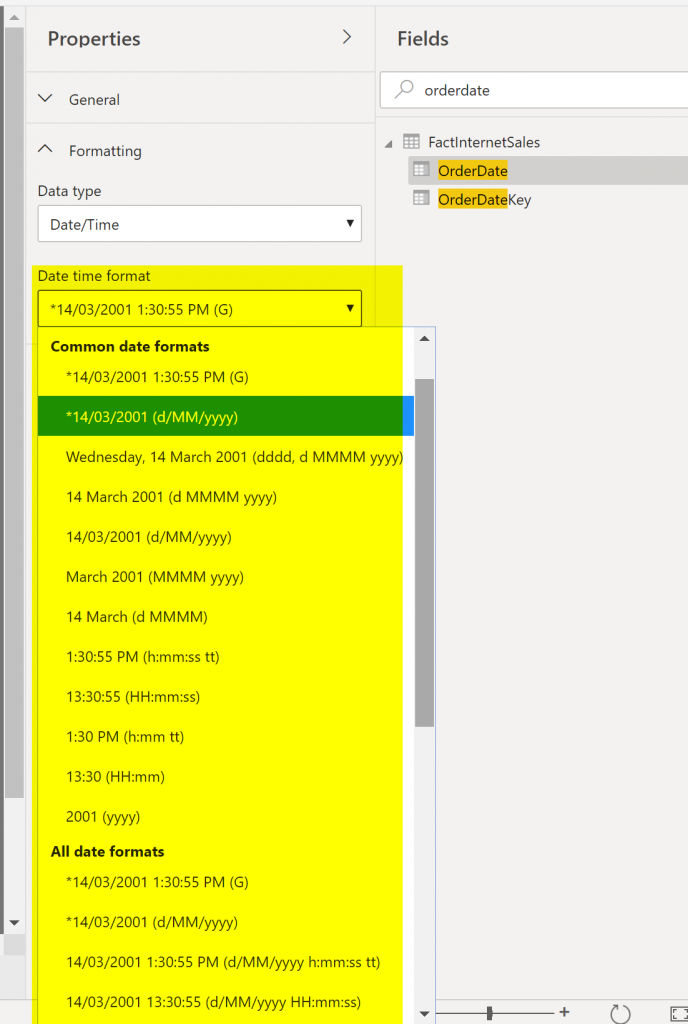
However, sometimes, you need a format, which is not there. In those scenarios, you can use Custom Formatting.
Custom Formatting
If you want to set any custom formattings, you can choose that option too. For a decimal field, for example, you can choose the format to be custom
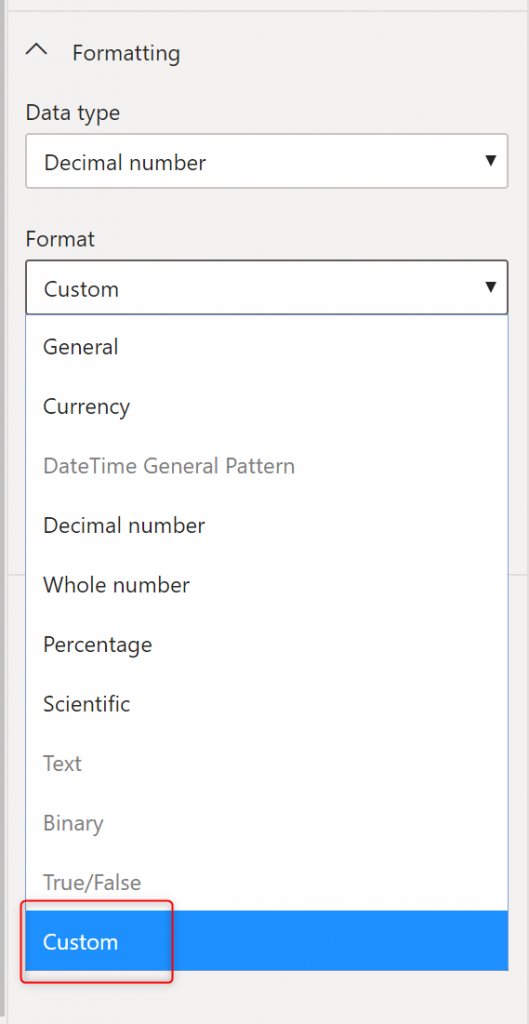
The custom formatting also comes with a few samples that you can choose:
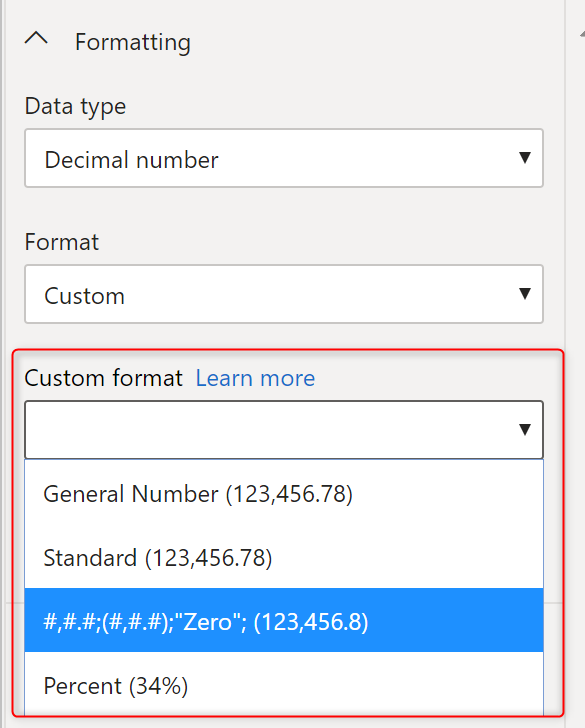
You can also customize it even more, and put your desired custom format. Let’s see how it works.
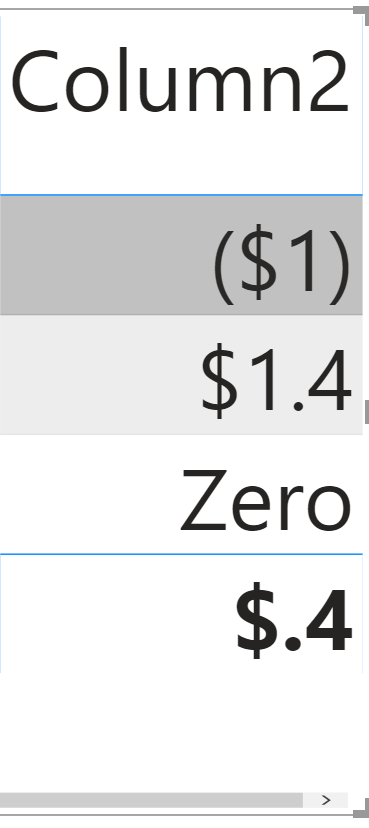
For example, here is the format you can try for decimal numbers:
$#,#.#;($#,#.#);”Zero”
there are three parts in the expression above:
<format for positive number>;<format for negative number>;<format for zero>
This would look like this in the visualization:
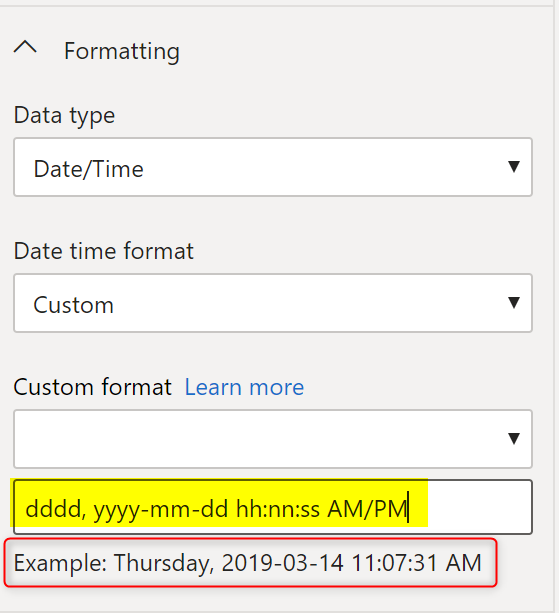
Custom Format on Date/Time fields
There are also formatting options for date/time fields. For example, the format string below will create the example showed underneath.
You can always try changing the format string, and see what the sample output looks like right underneath it.
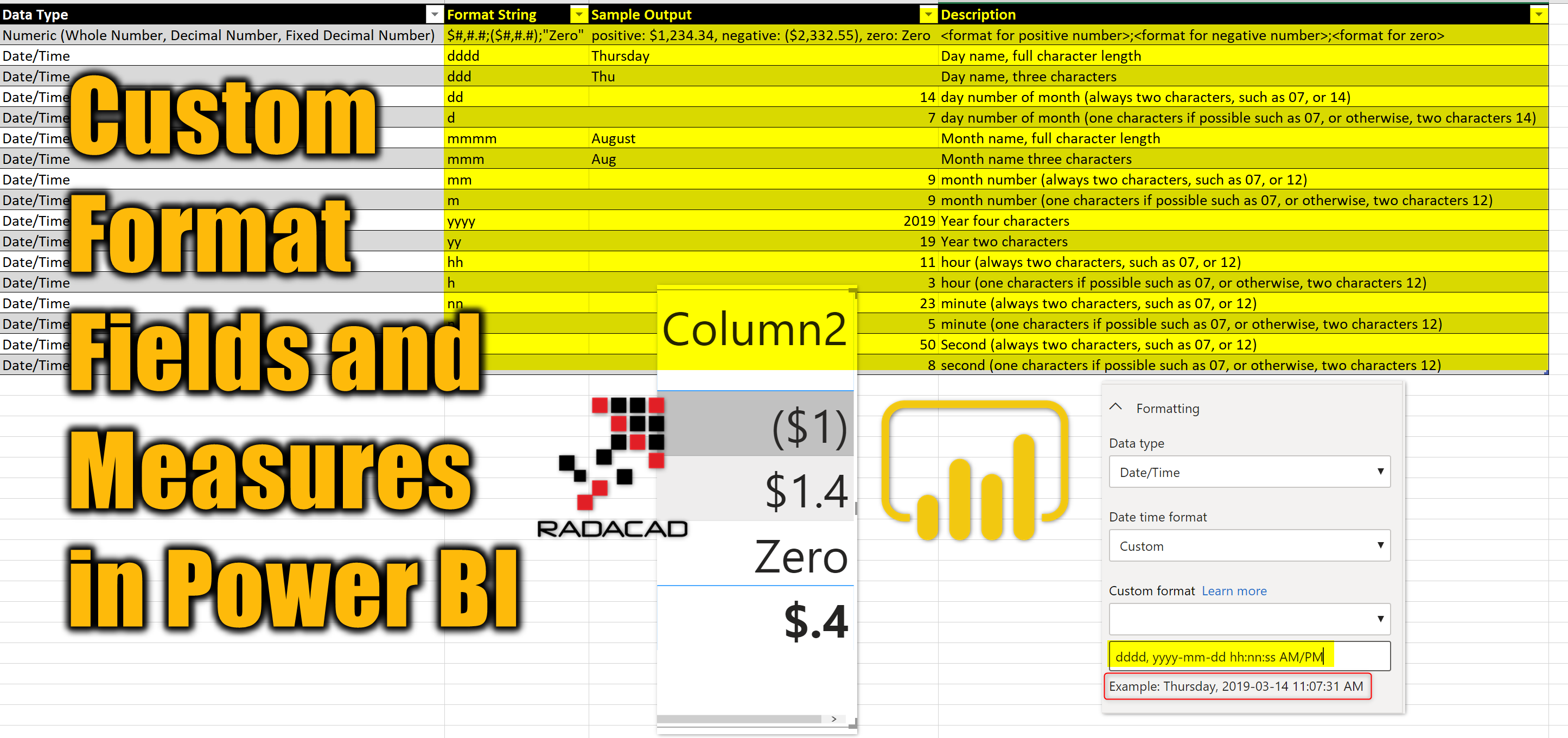
Custom Format String Table
The custom format string is built on top of the VBA format string, but not exactly all of that. Here are some of the format options you can use
| Data Type | Format String | Sample Output | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Numeric (Whole Number, Decimal Number, Fixed Decimal Number) | $#,#.#;($#,#.#);”Zero” | positive: $1,234.34, negative: ($2,332.55), zero: Zero | <format for positive number>;<format for negative number>;<format for zero> |
| Date/Time | dddd | Thursday | Day name, full character length |
| Date/Time | ddd | Thu | Day name, three characters |
| Date/Time | dd | 14 | day number of the month (always two characters, such as 07, or 14) |
| Date/Time | d | 7 | day number of the month (one character if possible such as 07, or otherwise, two characters 14) |
| Date/Time | mmmm | August | Month name, full character length |
| Date/Time | mmm | Aug | Month name three characters |
| Date/Time | mm | 9 | month number (always two characters, such as 07, or 12) |
| Date/Time | m | 9 | month number (one character if possible such as 07, or otherwise, two characters 12) |
| Date/Time | yyyy | 2019 | Year four characters |
| Date/Time | yy | 19 | Year two characters |
| Date/Time | hh | 11 | hour (always two characters, such as 07, or 12) |
| Date/Time | h | 3 | hour (one character if possible such as 07, or otherwise, two characters 12) |
| Date/Time | nn | 23 | minute (always two characters, such as 07, or 12) |
| Date/Time | n | 5 | minute (one character if possible such as 07, or otherwise, two characters 12) |
| Date/Time | ss | 50 | Second (always two characters, such as 07, or 12) |
| Date/Time | s | 8 | second (one character if possible such as 07, or otherwise, two characters 12) |




Thank you for sharing, this help me out for not creating new measures new columns into my Power BI Model in 2024!