The Power BI toolset comes in many shapes and forms. There is a Power BI Desktop, Power BI Mobile app, Power BI Report Server, and Power BI Service (and some other applications and components too). The questions I hear from the new users of Power BI are; Do I need to have an account for Power BI? do I need to use the Power BI website for creating visualization etc.? What is the Power BI website or service, and what is its usage? If I can do the reporting using Power BI Desktop for free, then why would I need the service? In this article and video, I will answer all of that.
Video
Power BI Desktop: Report Authoring Tool
The report authoring experience in Power BI is usually happening in the Desktop application called Power BI Desktop (Although these days, Microsoft is working hard to create a similar experience of it as a web version). Power BI Desktop is a tool you can install on your machine for FREE. You don’t pay a cent to use it. You don’t even need to have an account to use it. All you need is to download it and then install and use it.
Power BI Desktop has everything you need to create the report. However, the next step after creating the report is sharing it with others, even if that means just simply showing the result of it to others.
The Power BI files created in the Power BI Desktop can be saved as *.PBIX files, and then re-opened using the Power BI Desktop. However, You should not use that method to share the Power BI report with users. Because that means they need to install Power BI Desktop on their machines, there are some problems with that;
- Power BI Desktop is a report authoring tool. Even if the users can install it, they would have too much power; they can edit and change the report without knowing what they did. Then they would come to you to get their problem fixed.
- Users meant to use the report everywhere, their mobile devices, tablets etc. Power BI Desktop cannot be installed on all of these tools.
Hosting options for Power BI reports
To share the Power BI report correctly, you must host it somewhere. Then the hosted report can be viewed by the users using a web browser or the Power BI mobile application. This would be the right way of sharing the report and would not have the problems mentioned above.
There are two hosting options for Power BI reports; cloud-based hosting (called Power BI Service or website) and on-premises hosting (called Power BI Report Server).

What is the Power BI Service?
Power BI Service (or, as some call it, the Power BI website) is the cloud-based hosting environment for Power BI reports. This cloud-hosting environment is provided by Microsoft and is part of the Microsoft cloud service offering (Azure and Office 365).
In the Power BI Service, organizations are separated using Tenants. Tenants can be managed by Azure Active Directory or Office 365. Under tenants, there will be users. These users are Azure Active Directory users.
You can access the Power BI service at https://app.powerbi.com/.
In addition to users and authentications, there is the concept of workspaces in the Power BI Service. A workspace is like a shared folder between a team of users. This can be a place to share some of the Power BI content. There are many methods of sharing the Power BI content (that is published to the Power BI service).

Power BI Service allows security to be applied on the workspace or object level. There are tenant configurations and setting that can be applied to govern the entire organization’s usage of Power BI objects.
Publish reports to the Service
Reports created in the Power BI Desktop can be easily published to the Service. You can even create some objects only in the Power BI service, such as a dashboard as a landing page for multiple reports.
Capacity-based or User-based
To use the Power BI service, you must have a Power BI license. There are two types of licenses for Power BI; capacity-based and user-based licensing. The capacity-based licensing is usually better for organizations with more than hundreds of users, and user-based licensing is good for small to medium size businesses. Although, for some of the operations, in addition to the capacity-based licensing, you would also need to get some user-based licensing.
Power BI Service, Not just for hosting reports
Power BI Service is not just a place to host reports. It does much more things than that. Many of the enterprise features of Power BI were developed for the Power BI Service. Among these are components such as the list below;
- Dataflow
- Shared Dataset
- Datamart
- Metrics
- Data Lineage
- Content certification
- Sensitivity Labels
- Deployment Pipelines
- Workspaces
- Apps
- …
The components and features mentioned above are Power BI service-only features. They enable you to have a better governed Power BI adoption and a better architecture for the Power BI implementation. However, to use some of these, you may need premium licensing. In the below list, some of the most important items are explained.
Template apps
One of the useful features available in the Power BI Service is the template apps. Template apps are pre-built Power BI reports and models. Third parties have created these pre-built reports. You may need to purchase some of them to use them, but there are free template apps too. They would enable you to connect to your data source but without creating the report and getting the analysis ready.

Apps
Delivering the Power BI content to the user can be organized in packages called apps. Each app can contain multiple Power BI reports and content in it. The App can be designed with the back color and theme required, and you can set the landing page and audience of the app when creating it.
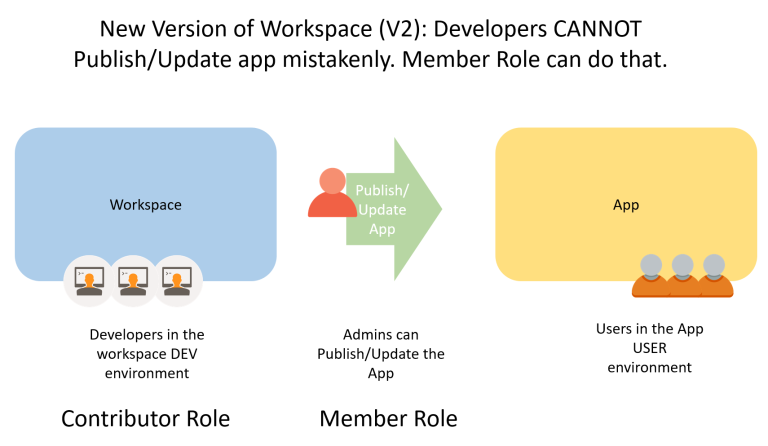
Workspaces
Power BI workspaces are collaborative environments for teams in the Power BI service. This is where the team can share the Power BI content, review and edit each other’s work, and deploy the changes to other environments. The team can have different levels of access in this shared environment depending on their role.
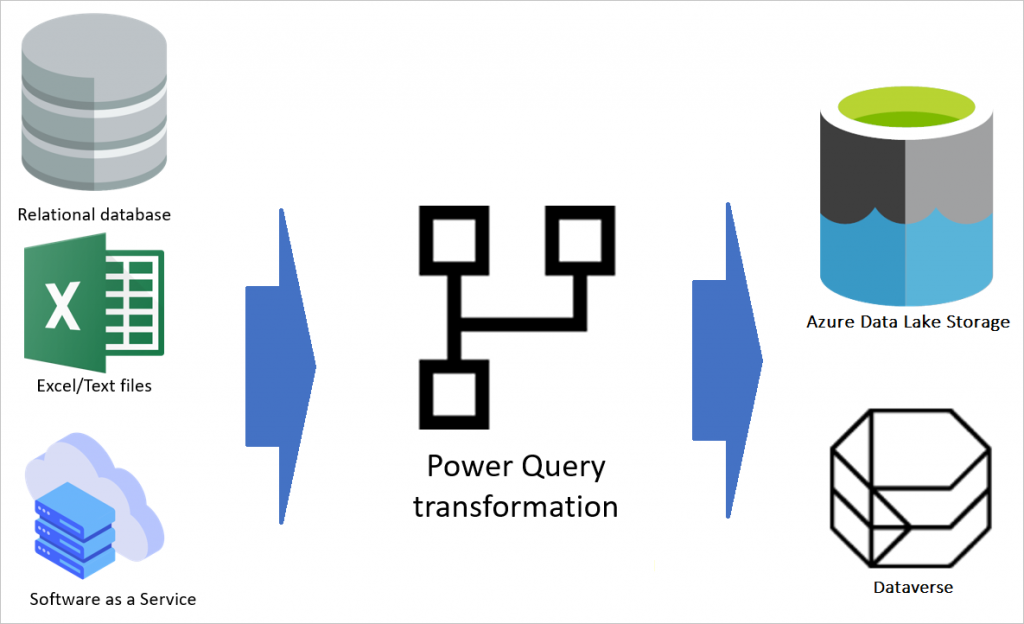
Dataflow
Dataflow is the cloud-based ETL using the Power Query engine. Instead of copying the data transformation between multiple Power BI files, you can use Dataflows for shared tables as a central place for data transformation and also storage of the data. Power BI files can get data from the Dataflow. Dataflow plays an important role in multi-layered Power BI architecture.
Shared Dataset
Once the dataset is published to the Power BI Service, It can be re-used to create a new thin report. A thin report is a report without a dataset, or in other words, a report that connects live to an existing Power BI dataset. When you use a dataset as a shared dataset, you can re-use the calculations and modeling done in that dataset in multiple reports. The shared dataset is also another important component of a multi-layered Power BI architecture.

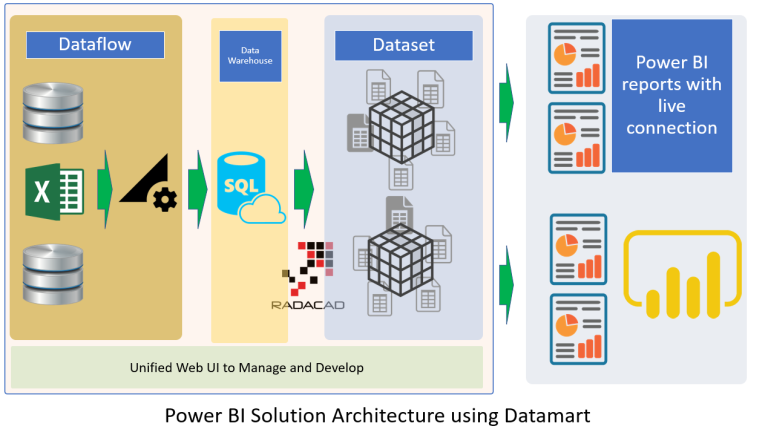
Datamart
Datamart makes the modeling of Power BI easier to manage by bringing all the configurations in the Power BI service with one unified editor to create the Dataflow and dataset altogether. The data also will be stored in Azure SQL Database, which comes as part of your Power BI licensing. Datamart is going to be the next generation of building Power BI models.
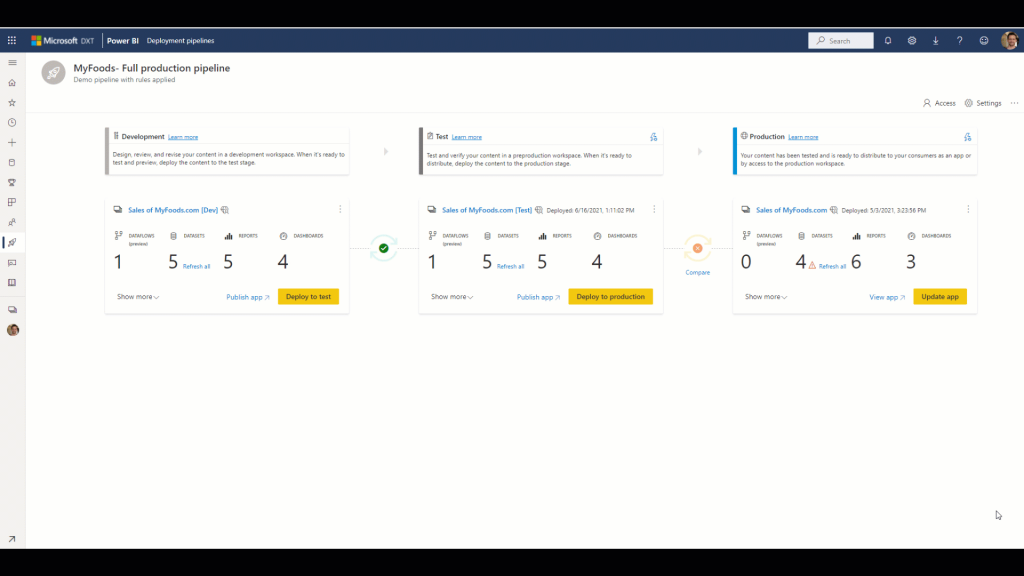
Deployment Pipelines
To ensure that users don’t get impacted by the changes done by developers immediately, it is essential to separate the Development environment from the User environment. In some organizations, this can be three environments of Dev, Test, and Production. When you have multiple contents in your Dev environment, pushing the changes into the next environment (Test or Production) can be managed easily using Deployment Pipelines. Deployment pipelines consider your Dev, Test and Prod workspaces and compare the changes between these environments and make the deployment easier to control.
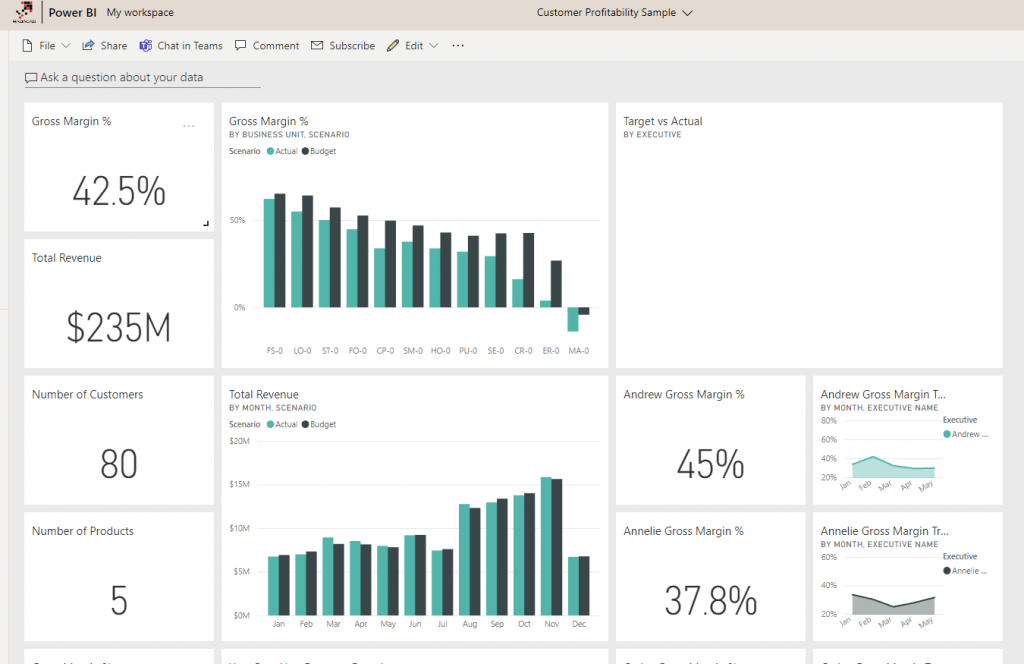
Dashboard
Power BI service offers another layer of visualization called Dashboard. The dashboard can be the landing page for multiple reports or can be used as a real-time visualization. Usage of the dashboard is optional; however, it comes with additional options such as Data Alerts and Auto-Refresh of tiles. Here I have explained the difference between a dashboard and a report.
Metrics
Power BI has a comprehensive component showing KPIs (Key Performance Indicators or metrics important for the business) or scorecards. This component was called Power BI Goals before and nowadays is called Power BI Metrics. Using Power BI Metrics, you can create all aspects of a KPI, such as value, target, trend, status and rules that define if the value is on track or behind etc. The metric can use a Power BI shared dataset as a source.

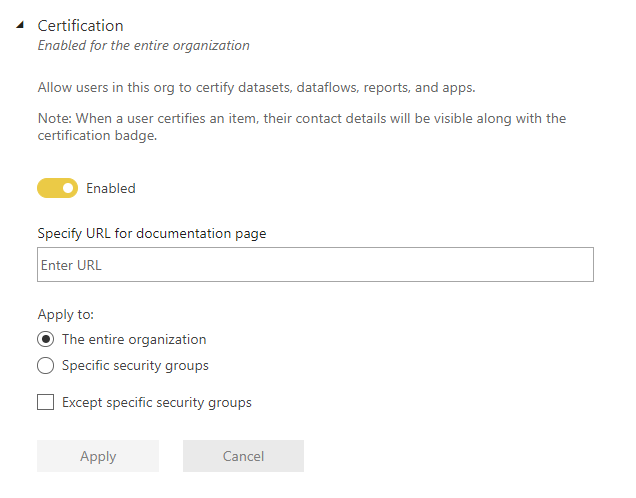
Content Certification
Power BI service also offers some data governance settings and configurations. One of these is called content certification. Power BI objects such as datasets, dataflows, reports and apps can be certified by a certain group in the organization. The Power BI tenant administrator can control the roles certifying the content. This helps in the adoption and usage of the content by other users to find reliable content.
Data Lineage
As there are many data-related components available in the Power BI service, one may easily get lost that where the data of this visual in this report is coming from, which dataset and dataflow fetch that and from what data source it is coming. Power BI Service offers a data lineage that can be used to find details. The lineage is still a work in progress and would enhance more in the future, I believe, as some cases aren’t supported yet.
Summary
Power BI Service is one of the two hosting options for Power BI content. Power BI service hosts the Power BI content in the cloud and is used in the majority of cases instead of Report Server (which is the on-premises hosting solution for Power BI content). Power BI service comes with all the features and configurations needed for a hosting platform (user access, tenant-level configurations, workspaces, categorizing the content, sharing etc.). It also comes with extra useful features and components. These extra components are playing a very important role in Power BI adoption and implementation; some of these components are; Dataflows, Shared Dataset, Datamart, Metrics, Dashboards, Deployment Pipelines, Content Certification, Workspaces, Apps, etc. These extra components and the regular update of the Power BI service make it an important part of the Power BI adoption in many organizations.
At RADACAD, we deliver many Power BI courses and consulting for customers all around the world; if you wish us to organize training for your group, or help you in your data analytics path, contact us.
Are you using Power BI service in your Power BI implementation? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.